Historical disasters
| Site: | Spark: piattaforma di e-learning del Liceo Majorana |
| Course: | eHAND: Effects of Human Activities on Natural Disasters |
| Book: | Historical disasters |
| Printed by: | Utente ospite |
| Date: | Wednesday, 18 February 2026, 8:55 AM |
Description
article
1. Historical disasters in Europe
Europe has had an immense number of natural disasters to overcome. Most areas in Europe have dealt with floods and strong storms, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions in their past. Natural disasters could have a huge impact on the past: they could ruin cities or regions, even eradicate entire civilizations and leave tens of thousand dead or homeless.
Ten deadliest natural disasters
2.Earthquakes
3.Eruptions
4.Floods
5.Landslides
6.Storms
6.1. Reunion7.Fires
8.Invasive species
8.1. Portugal2. Earthquakes
Europe has a long history of destructive earthquakes.
Italy, the Balkans, Greece, Bulgaria, Romania and Turkey are among the most exposed regions of the continent.
2.1. Greece
The high seismic activity of the country is due to the fact that it is located at the boundary of the Africa-Eurasia convergence. Within this framework, the Anatolian plate rotates counterclockwise. From the west, the Adria microplate rotates counterclockwise. As a consequence, the Aegean a general compressional stress field and the inner Aegean area experiences a general extensional stress field.
Greece often hosts large magnitude earthquakes, whilst a moderate or small magnitude earthquake is felt every 2-3 days on average. Although the majority of these earthquakes are shallow, a few cases have been recorded as «devastating» for the human environment or for life loss (e.g. the 1881 Chios, 1953 Kefalonia, 1999 Athens earthquakes). No historical information is provided for extensive migration of populations and obliteration of civilizations in Greece due to earthquakes.
 |
 |
|---|
Assiros, Thessaloniki 1902 Earthquake measuring 7.9 on the Richter scale struck on August 11, 1902 the area of Assiros in Thessaloniki. Five people were killed.The damage to brick buildings was big,especially in Assiros as well as in Langada and in Agios Vasilios. In Thessaloniki many buildings had problems as well as the port, but only few of them had serious damages. The largest of the cracks observed in the soil had length 100m.
Athos, Chalkidiki 1905 In november 1905 a 7.5 Richter scale earthquake hit the Mt. Athos Peninsula. The epicentre was located near the monastery of Stavronikita as to be seen on this map. There was damage in Karyes, Lavra, Kavsokalivia and many other places. The earthquake caused also a huge stone avalanche on the south slope of the mountain near Ag. Nelios.
Ierissos, 1932 The 1932 Ierissos earthquake occurred at 19:20 on 26 September. It caused severe damage in Ierissos and the surrounding part of the Chalkidiki peninsula, with 491 casualties reported. The Aegean Sea is an area of mainly extensional tectonics caused by the subduction of the African Plate beneath.The earthquake has been attributed to movement on the Stratoni fault, one of the W-E trending faults that shows predominantly dip-slip extension. The earthquake destroyed the town of Ierissos and several villages in the surrounding area. 10,000 people were left homeless. The cost of the damage was estimated at 5 million drachmas. The 1932 Ierissos earthquake occurred at 19:20 on 26 September. It caused severe damage in Ierissos and the surrounding part of the Chalkidiki peninsula, with 491 casualties reported. The Aegean Sea is an area of mainly extensional tectonics caused by the subduction of the African Plate beneath.The earthquake has been attributed to movement on the Stratoni fault, one of the W-E trending faults that shows predominantly dip-slip extension. The earthquake destroyed the town of Ierissos and several villages in the surrounding area. 10,000 people were left homeless. The cost of the damage was estimated at 5 million drachmas. The earthquake was followed by three strong aftershocks (M=6.0, 5.7 & 6.2) in the period 26–29 September, and the largest (M6.3) on 11 May of the following year.
Thessaloniki, 1978 The Great Thessaloniki earthquake occurred on 20 June at 23:03 local time. The shock registered 6.2 on the moment magnitude scale, had a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent), and was felt throughout northern Greece, Yugoslavia and Bulgaria. It was the largest event in the area since the 1932 Ierissos earthquake.The epicenter was 20km east of Thessaloniki between lake Koronia and Volvi, in the village of Stivos. It lasted 10 seconds. There was a series of pre-earthquakes with stronger that of size 5.8 degrees on the Richter scale on 25-05-1978 which caused damages on buildings such as the cathedral of Thessaloniki. It also followed a series of powerful aftershocks with stronger that of 5. degrees on the Richter scale in 7-05-1978 with epicenter the Lake of Koronia (7,0 - 10,0 km from the town).
49 were dead, 220 were injured, 800.000 were left homeless either because their homes were destroyed or because they did not dare to use them. The collapse of a eight-storey building in Hippodrome Square wreaked havoc as 29 were killed out of the total 49 victims. Moreover, there have been serious damages in historic sites such us Rotonda, the church of Agia sofia and Church of the Acheiropoietos. The total cost of repair was estimated at 3-5 billion euros.
2.2. Italy
Italy is a very seismic territory and the main history earthquakes were
Messina on 28 December 1908 The most devastating earthquake took place in Messina, his magnitude was 7.1 and between 75,000 and 200,000 lives were lost. The earthquake almost levelled Messina and Reggio Calabria. About ten minutes after the earthquake, the sea on both sides of the Strait suddenly withdrew and a 12-meter (39-foot) tsunami swept in and three waves struck nearby coasts. It impacted hardest along the Calabrian coast and inundated Reggio Calabria after the sea had receded 0 meters from the shore. In Messina, the tsunami also caused more devastation and deaths. The disaster affected the local economy and Messina faced a temporary depopulation after so many homeless survivors had sought refuge elsewhere.In the years following 1908, precautions were taken when the reconstruction of Messina began in 1909, building architecture that would be able to withstand earthquakes of variable magnitude, if one should strike again. Initially, authorities adopted a plan to demolish the remaining structures of Messina and transfer the city and its port elsewhere in Sicily but this was discarded after strong protests from the Messina
2.3. Portugal
Some of the earthquakes with more impact in the history of Portugal
Azores earthquake – 1980 71 people died, 7.2 on the Richter scale, 70% of the houses on Terceira (one of the islands) were completely demolished.
Setúbal earthquake – 1858 Very destructive, 7.1 magnitude.
Lisbon earthquake – 1531 Very violent, with a tsunami, 30.000 mortal victims.
The Lisbon earthquake, 1755 This is the most intense earthquake that has ever occurred in Portugal. It occurred on Saturday, November 1st. Today the seismologists estimate that this earthquake had a magnitude around 8.5 on the Richter scale. In combination with subsequent fires and a tsunami the earthquake almost totally destroyed Lisbon and affected adjoining areas killing more than ⅓ of the population of the city. Even though it caused the most damage in Lisbon it was also particularly destructive in Morocco where approximately 10,000 people lost their lives.
The reconstruction of the city
The Pombal marquis was the one responsible for organizing the reconstruction of the city. He occupied the charge that now is equivalent to Prime-Minister. The king at the time was José I but it was under the command of Marquess of Pombal (Sebastião José de Carvalho e Melo) that the city, mainly the downtown, was rebuilt and redesigned by architects. Some buildings were built with anti-seismic technology, which was really innovative at that time.
2.4. Romania
In terms of seismicity, Romania is considered to have a moderate seismic activity, given its geographical position and its closeness to a convergent plate boundary. Being situated in a seismic active region, Romania has a history of devastating and deadly earthquakes. The Bucharest area has experienced a number of earthquakes of varying intensities, and the probability that a severe and damaging earthquake will occur is high.Photographs from the 7.2 M on the Richter Scale Earthquake in Bucharest, Romania which resulted in 2000 deaths in 1977.
 |
 |
|---|
The cause of earthquakes is clearly the geographical location of Romania which is situated close to a convergent plate boundary at the convergence of the East European Plate (EEP), Moesian microplate (MoP), and Intracarpathian microplate (IaP) which seem to meet into the Vrancea area (South-Eastern part of the country), whose active seismicity has been considered to be due to the presence of a continental unstable transform-transform-compression triple-junction. Thus, the Vrancea region, located in the South-Eastern part of the country is especially high in earthquakes and traditionally has been the epicenter of many earthquakes. Moreover, the Romanian volcanoes (the Carpathian Mountains) are active at a convergent plate margin. The Eastern Carpathians volcanic arc is 160 km long, the longest in the entire Carpathian mountain belt and it formed as a result of the convergence between two plate fragments, the Transylvanian micro-plate and the Eurasian plate.
2.5. Turkey
Turkey is located in one of the most actively deforming regions in the world. The tectonic in and around Turkey depends on relative motions among the African, the Aegean, the Arabian, the Anatolian, the Black Sea and the Eurasian plates.
The neotectonics of Turkey is directed by three major elements :
1) The Aegean–Cyprean Arc, a convergent plate boundary where the African Plate to the south is subducting beneath the Anatolian Plate to the north;
2) The North Anatolian Fault Zone;
3) The East Anatolian Fault Zone
61% of the natural disasters in Turkey is Earthquakes .
From past to now, a lot of major earthquakes occurred in our lands. The biggest earthquake which occurred in Turkey was 8 magnitude. It was occurred in Antakya.This is the major eathquakes list.
MAJOR EARTHQUAKES
Antakya
(Antioch) Earthquake, 115 CE The
most damaging earthquake in Turkey was on
December13,115.Approximately 260,000 people lost their lives in the
7.5 magnitude earthquake.This earthquake is one of the more famous of
the ancient times, because it hit a major city of the Roman Empire
and the emperor Trajan was in the city when happened.
Antioch(Antakya) and surrounding areas were devastated
with a great loss of life and property. It was felt all over the
near East and the Eastern Mediterranean .
29 March, 526 Antioch Earthquake
The estimated magnitude for the earthquake is 7.0 .It was followed by 18 months of aftershocks. The city was very crowded because a lot of visitors come to celebrate Ascension Day.
Since it was the time of dinner a lot of people were in their home or inside areas more than 250.000 people died in this earthquake. The earthquake was followed by a fire that destroyed most of the buildings left standing by the earthquake.
This number is a terrible figure for that period,because it is the biggest disasters in the history of the World.
The earthquake caused severe damage to many of the buildings in Antioch.Only houses built close to the mountain are said to have survived. Most of the damage however, was a result of the fires that went on for many days in the immediate aftermath of the earthquake, made worse by the wind.The Great Church was destroyed by the fire seven days after the earthquake.
Istanbul Earthquakes in the Middle Ages

Severe earthquakes that took place on 19 October and 14-23 December 554 in Istanbul, followed by the aftershocks that followed, gave the Byzantines 40 days of great fear.
Many churches were destroyed by the walls and Hebdemon (Bakırköy) and the dome of Hagia Sophia was damaged.
In the violent earthquake of 740 the Hagia Irini church was damaged;
The ephemeral tremors of 869 also lasted forty days at intervals. The Byzantines thought that earthquakes were a punishment sent against the sins they committed. They tried to prevent earthquakes through various rituals, ceremonies and rituals, and also organized religious special memorial anniversaries and made them part of the liturgical (religious) calendar. Along with few, some Byzantines influenced by Aristotle's theory believed that earthquakes were caused by natural causes (movement of underground winds)
Anatolian-Syria-Aleppo Earthquake (1138):

It is estimated that more than 200.000 people have died in this severe earthquake that erupted in Aleppo on 11 October 1138. In addition to Anatolia, the great earthquake in Syria has also caused the city of Aleppo to be destroyed. It is known as one of the most deadly earthquakes in the history of the world.
Istanbul Earthquake(1509)( small apocalypse)
Istanbul has been exposed to a great number of depressions throughout history, some of which are severe.
Because this city is located on major fault lines.
This earthquake had an estimated magnitude of 7.5 magnitude
It caused great destruction, loss of life and fear, became a small apocalypse (apocalypse) and took place on 22 August 1509; Aftershocks continued throughout the next year. This earthquake, which broke the Marmara fault line along the length of the sea, felt a very wide area from Anatolia and Egypt to Greece and Austria. This earthquake, which is the center of the Marmara Sea and has effect on the area from İzmit to Tekirdağ.It took place on May 22, 1776 after the second day of religious day of muslims. the earthquake that took place in a terrible noisy meeting, strong fluctuations (tsunami) occurred in the Bosphorus. After this great earthquake, in the Ottoman capital 1767, 1768, 1769, 1771, 1790, 1802, 1804, 1837, 1841 (severe) and 1855, respectively, experienced severe earthquakes and minor damage and loss of lives. On the other hand, in 1789 III. Selim ordered the building not to be built too high in the capital.
Istanbul (Marmara) Earthquake (1894): This eartquake occured on July 12th.It was 7 magnitude.1349 people died in this earthquake.At the request of Abdulhamit, Egnitis, the Director of the Athens Observatory, and Kumbari, the Director of the Observatory, prepared a scientific report on the disaster and sangayat. On the other hand, after the earthquake, the first seismological observatory of the Ottoman State was established.Professor Agamemnone, geodynamic expert from Rome, came to Istanbul to work with the Director of the Observatory, Coumbary and was involved in seismology studies. The results of the earthquake disasters were sometimes tried to be shown lightly by the state administrations. As a matter of fact, II. Abdülhamit also applied censorship to the press on earthquake news. 1894 catastrophe Even though it is not the biggest earthquake in Istanbul, the Byzantine daylm carries the title of "last violent earthquake". It is also the most studied and researched earthquake in Istanbul between the 30 earthquakes leading to the loss of life and property.THE BIGGEST EARTHQUAKES IN TURKEY in the last Century
1-1939 Erzincan Earthquake
2-1944 Bolu Gerede Earthquake
3-1983 Earthquake in Erzurum
4-1999 Gölcük Earthquake – Izmit
5-1999 Düzce Earthquake – Bolu
6-2011 Van Earthquake7-2017 Çanakkale Eartquakes
1939 Erzincan Earthquake;
Among the earthquakes that lived in the Anatolian lands, the disaster of Erzincan in 1939 has a special place. That year, the number of dead reached 33.oo0 in Erzincan, which is one of the places that connects December 26 to December 27. This earthquake magnitude was 8.
This earthquake, considered one of the great earthquakes in the world, .It was the most serious and devastating earthquake disasters in Turkey. Both Erzincan and the other 11 cities was affected from that earthquake and big losses took place.During the earthquake, the city's railway bridge was destroyed, the telegraph lines were broken, and the entire relationship with Erzincan's surroundings was completely cut off. So the earthquake can be learned after hours. After the repair of the destroyed bridges, the aid teams could only enter the city on the 28th of December.1944 Bolu Gerede Earthquake; On February 1, 1944, a total of 3 thousand 959 people were killed, 182 people were injured and 9 thousand 422 buildings were destroyed as a result of the earthquake of 7.4 magnitude according to Richter scale in and around Bolu.
1983 Erzurum Earthquake, on October 30, 1983, caused massive damage to Erzurum a significant loss of life 155 thousand people died, 537 people were injured, 3 thousand 241 houses were heavy, 3 thousand houses were medium and 4 thousand houses were slightly damaged and more than 30 animals were lost in this earthquake of 6.9 magnitude
1999 Gölcük Earthquake; Gölcük Earthquake, Izmit Earthquake or Marmara Earthquake, took place in the morning of 17 August 1999 at 03:02 local time. Kocaeli Gölcük-based earthquake of 7.5 magnitude, caused large-scale loss of life and property. August 17 Earthquake was felt in the entire Marmara Region, from Ankara to Izmir. According to official reports, 17 thousand 840 people were killed and 43 thousand 935 people were injured. 505 people were disabled. 285 thousand 211 housing, 42 thousand 902 business sites were damaged.
1999 Düzce Earthquake; This earthquake, which lasted for about 30 seconds and had a magnitude of 7.2, took place on the segment of the northern limb of the North Anatolian Fault that caused the August 17, 1999 earthquake. November 12, 1999 earthquake, the breakdown of August 17, the eastern part of the Düzce fault triggered development.
After 87 days of the Marmara Earthquake, a second earthquake was unseen in the history of the world while trying to hug the earthquake. This time the epicenter was the center base Düzce. When Time 18: 57 showed, Düzce was shaken by a powerful blow, almost within 30 seconds it became a place. Earthquake, while Kaynaşlı place, the loss of life and property in a part of Bolu caused
2011 Van Earthquake: One of the major earthquakes in Turkey that has survived to the present day and cost a lot of people lives in Van on 23 October. 604 people lost their lives in the earthquake, which is the center of Ercis, which is 7.2 times the size of the center, and 222 people were rescued right from the wreckage. While trying to hug the massive earthquake wounds, this time a second earthquake of 5.6 magnitude centered on Edremit on November 9th. Thirty-two people lost their lives in this earthquake, and 30 people were removed from under the debris to the right.
3. Eruptions
There are currently over 60 active volcanoes located throughout Europe, and two of the world most active volcanoes are located in Italy. A volcano can be classified as active, dormant or extinct. An active volcano is one that has erupted in recent history, while a dormant volcano is one that has erupted in the past, but does not show any signs of activity. An extinct volcano is one that is not believed to have the potential to erupt again.
Volcanic Eruptions Triggered Crises Throughout European History
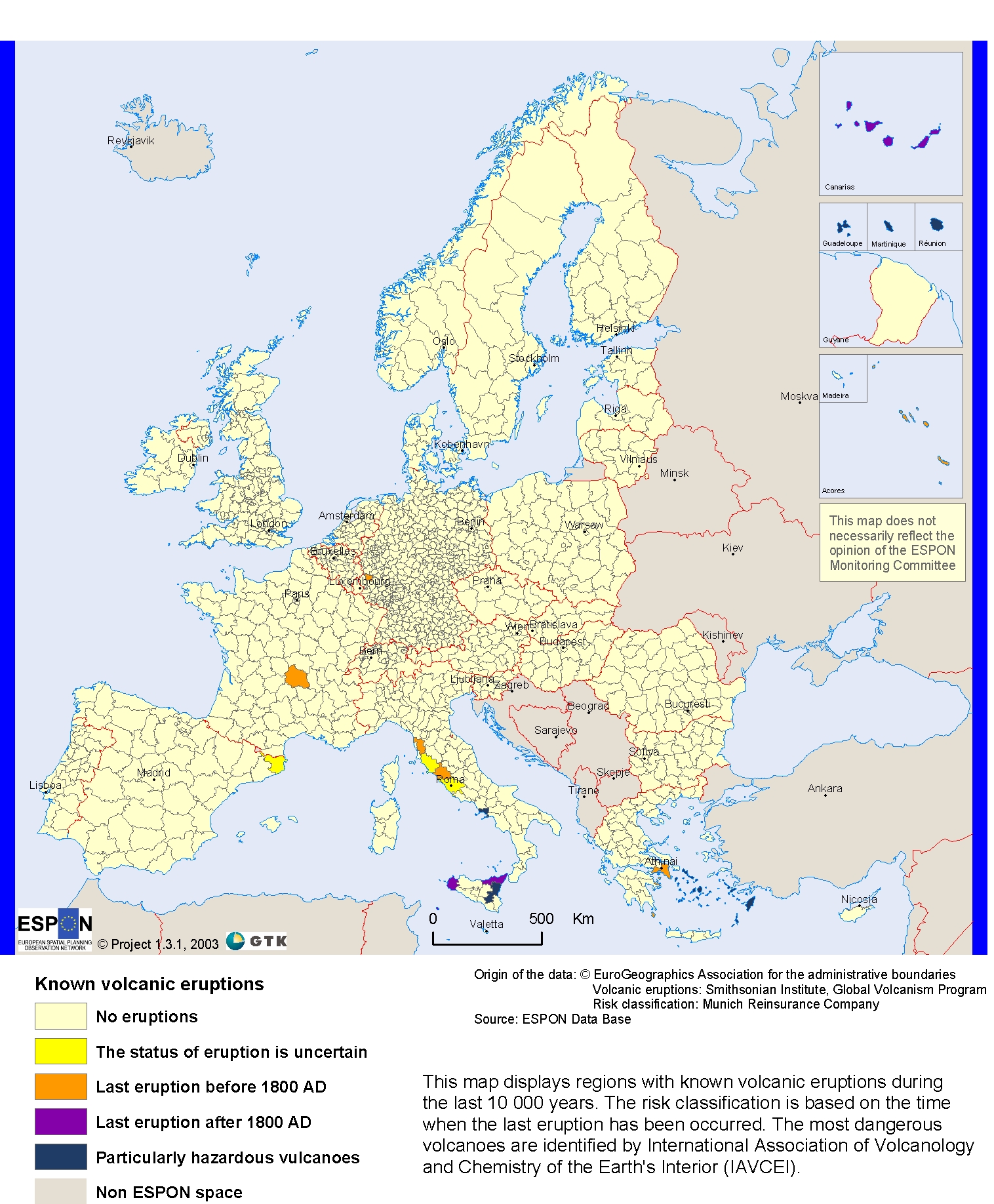
3.1. Greece
The Minoan eruption in Santorini.
The Minoan eruption happened around 1645 BC in the Late Bronze Age. It was one of the largest plinian eruptions in younger time. It erupted ca. 30-40 km3 rhyo dacitic magma and is ranked VEI=6 (Volcanic Explosivity Index after Simkin and others, 1981). The eruption was followed by collapse of the magma chamber that enlarged an existing caldera .The height of the plinian eruption column is estimated 36-39 km (Pyle, 1990). It dispersed tephra throughout the Eastern Mediterranean and might have led to global climatic impacts. Its deposits on Santorini consist of up to 50 m thick layers of white pumice and ash. The eruption destroyed an inhabited and culturally high-developed island which perhaps might be the origin of the Atlantis legend as many scientists believe. Since 1969 excavations near Akrotiri have brought to light an important marine Cycladic town famous for its well-preserved and magnificent wall-paintings
3.2. Italy
Italy is a volcanically active country, due to the presence of the boundary between the Eurasian Plate and the African Plate
The main history eruptions:
The eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD was one of the most catastrophic volcanic eruptions in European history. Historians have learned about the eruption from the eyewitness account of Pliny the Younger, a Roman administrator and poet.
Mount Vesuvius spewed a deadly cloud of volcanic gas, stones, and ash to a height of 33 kilometres ejecting molten rock and pulverized pumice at the rate of 1.5 million tons per second.
The eruption completely destroyed Pompeii, Herculaneum, Stabiae and Oplontis.
By 2003 around 1,044 casts made from impressions of bodies in the ash deposits had been recovered in and around Pompeii, with the scattered bones of another 100. The remains of about 332 bodies have been found at Herculaneum (300 in arched vaults discovered in 1980). What percentage these numbers are of the total dead or the percentage of the dead to the total number at risk remain completely unknown.
Pompeii and its inhabitants were well-preserved for almost two thousand years. The lack of air and moisture let objects remain underground with little to no deterioration. Once excavated, the site provided a wealth of source material and evidence for analysis, giving detail into the lives of the Pompeiians. However, once exposed, Pompeii has been subject to both natural and man-made forces, which have rapidly increased deterioration.
3.3. Portugal
In continental Portugal there are no cases of active volcanism besides thermal springs (secondary volcanism) that are pretty common. However, there are volcanic events in the Azores islands. That's because they’re volcanic islands and 9 of the volcanoes that formed them are still active. Submarine eruptions are not rare and there are plenty of cases of secondary volcanism on the islands like fumaroles or thermal springs.
T
he
Capelinhos eruption
This is the most intense volcanic eruption to have ever happened in Portugal. It occurred in Faial, one of the islands of the Azores archipelago. It happened on 27th September 1953. This eruption was of the explosive type. These eruptions are characterized by the big quantities of pyroclastic material (varying from rocks to dust) and gas released. Following a 2 day intense seismic period with more than 200 earthquakes, of an intensity not exceeding V of the Mercalli intensity scale. There were a lot of buildings affected: broken windows, tiles falling from roofs. Cultivated fields were covered with a thick layer of ash. However, there were no victims. The affected people were forced to migrate significantly between 1957 and 1960.
3.4. Reunion
1986 : St Philippe
Reunion
island is a volcanic island. we have two volcano but only o
ne
is active which is the Piton de la Fournaise.
We have a lot of historical eruption but we will introduce you only the biggest. f course we have many other historical eruption of our volcano but we can introduce you all of them. Since January 31st we have a volcanic eruption and it continue.
4. Floods
Floods in Europe have caused deaths and damage across the Countries. Such events are likely to increase in Europe for several reasons including climate change, according to recent assessments from the European Environment Agency (EEA).
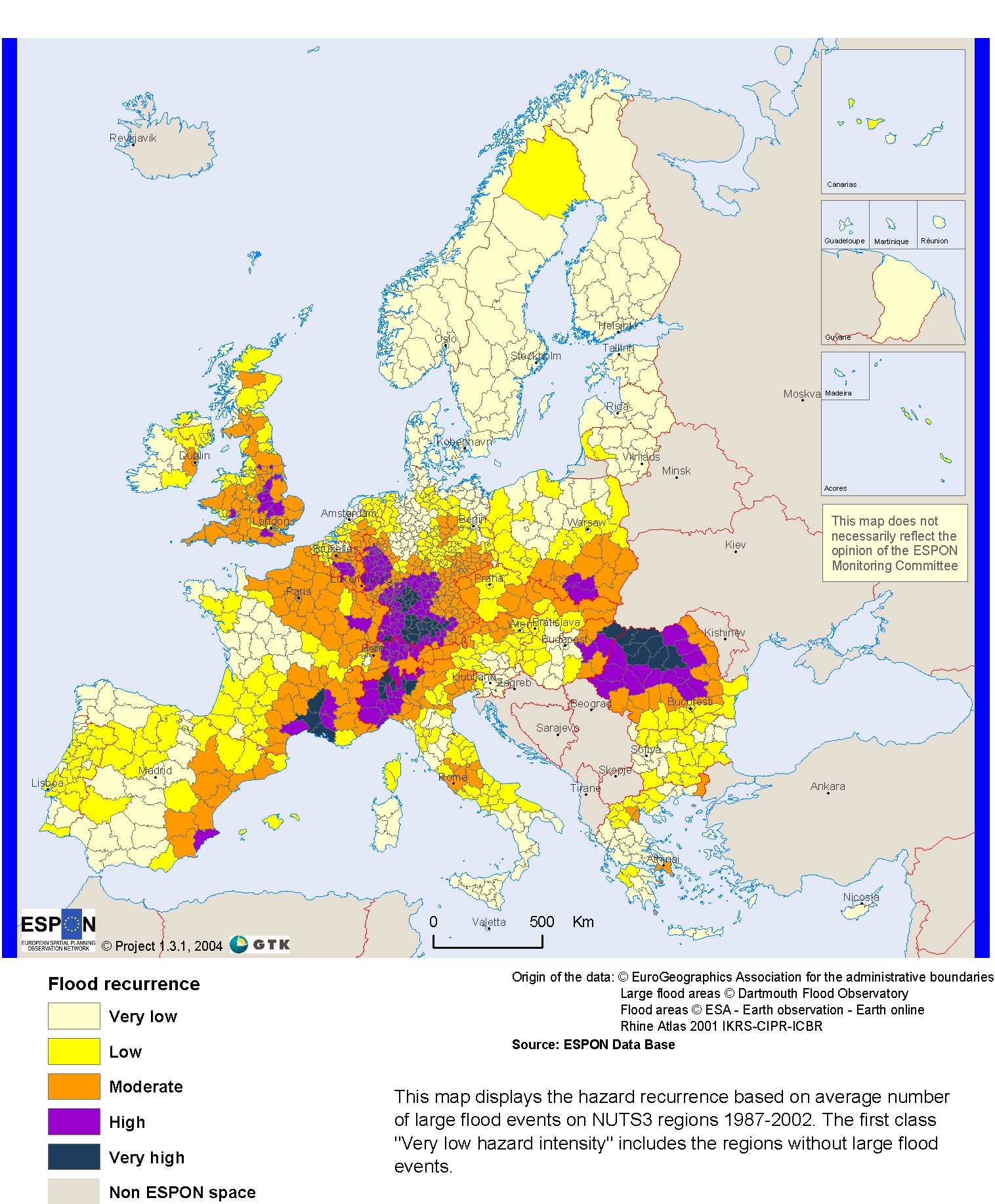
4.1. Greece
As a country, Greece has suffered from numerous floods, which have caused many people to become homeless. Not to mention the fact that floods have killed a considerable number of people.
From Greece's mythology, the first ever flood which occurred was named “The Ogygios Flood”. It happened in Voiotia and it killed lots of residents living there, but not King Ogygios, whom the flood was named after.
Despite Greece's vulnerability to major floods, it has mainly suffered from flash floods. A flash flood is a rapid flooding of geomorphic low-lying areas: washes, rivers, dry lakes and basins. It may be caused by heavy rain associated with a severe thunderstorm, hurricane, tropical storm, or meltwater from flowing-over ice sheets or snowfields. Flash floods can occur in unexpected times and are very deadly concerning the destruction ice or snow can create.
Here in Oraiokastro, we have been struck by floods on numerous occasions during the last years, but we were prepared and, luckily, no one was hurt. It is very likely that our landscape and high altitude are the reasons why floods are very susceptible to occur, especially during the autumn.
4.2. Italy
Italy is a country that suffers hydrogeological instability: floods and landslides.One of the most important flood historical event in Italy is when the Arno flooded Florence in 3 and 4 november 1966. The flood was caused by the intensive rains of the previous days. The consequences of that tragic event were very serious. The flood caused 48 deaths, 5 missings and 46.600 displaced, caused enormous damages in the all Tuscany, and in particular to the historical and cultural capital Early in the morning of the 4th November, in the old town centre of Florence there was 3 metres of water and mud. The flood caused a lot of deep damages to the artistic assets of the city :1200 artworks, 2 millions of important volumes and 1600 m2 of frescoes were submerged in the mud. The artworks were ruined gravely because citizens and business owners were warned late. In the following days a lot of rescuers came from every part of Italy and from all the World to take assistance to the citizens. A lot of volunteers salvaged and secured the artworks submerged in the mud in the storage rooms of the Uffizi museum. The most terrible damages were in the National Central Library and in the Cavalleggeri square. Fortunately some volumes and manuscripts were recovered, but on the other hand a lot of them were destroyed in the mud. The restoration of Florence continued for many years.
4.3. Portugal
Floods are temporary and natural phenomena, caused by moderate rainfall and permanent or sudden and high-intensity rainfall. This excess rainfall does increase the flow of water, giving you a little nervous of the normal bed and flood the banks and surrounding areas. In some parts of the globe the floods may be due to the melting of ice caps.
Portugal suffered severe floods in the past, and other natural disasters that caused serious problems like thousands of victims and much destruction due to weak structures and the few rescue and prevention techniques.
The most affected areas in Portugal are Porto, Vila Nova de Gaia and Peso da Régua.
Historic floods in Lisbon
• Lisbon is the City that had more occurrences of landslides in the last 150 years. From 1865 until 2015, the capital has registered 56 landslides that caused 32 dead, 125 evacuated and 402 homeless.
• It is the biggest scientific survey of floods and landslides that caused deaths in Portugal in the last century and a half.
• Lisbon is a very conducive to this type of disasters because the topography and the geology are complicated. The solo features not much consolidated sedimentary rocks, tilted with the slope of the strands.
Historic Floods in Porto
• These floods occurred in the Porto, on the banks of the Douro River, due to the huge increase in the barrage of Crestuma.
4.4. Reunion
Floods, which are overflowing of water recovering a place, are a major natural’s risk in Réunion IslandIn Reunion Island ,important floods risks exist . And those floods constitute the major natural’s , the more frequent and the more destroyer risks of the Island . Due to this water’s surplus , we can observe differents types of phenomenons :
- first , floods caused by overflowing , ,gullies :
-then , floods by rise of phréatic table:
- sea's floods due to hurricanes and cyclones:
Reunion Island , is concerned by rains of an exceptional intensity . Those importants rains are the most of time due to the tropicals cyclone’s passages.
Historical floods :
First from 1800 to 2000 in 2 centery we count 104 floods in Reunion islands,
In 1829 , due to a cyclone , all the harvest are engulfed by waves:
In 1878 , due to an other cyclone , and by the floods , a lot of families are taken by torrents , the were more than 50 millions.
In 1880 hyacinthe cyclone due to this 3 passages on the Island , he caused extreme rains which provoked important floods
In 2007 , gamede caused ,important flood which destroyed bridge of the st etienne river ,and (provoked 100 millions of disaster , and they were also two victims of waters:
In 2013 felleng hurricane provoked important flood which destoyed roads:
4.5. Turkey
The
floods are actually natural and normal environment events. The
contribution of mankind plays a great role in turning this nature
event into a disaster. Some of the great floods that took place in
many parts of our country from past to now.
ISTANBUL 24 August 1553, it gave a big harm to the city.In 1563 and 1750 another flood hit İstanbul .However, the flood in 1789 was a great disaster. 64 people died.houses and baths were destroyed. Edirne floods FOR YEARS ,After the heavy raining in GREECE and BULGARIA , Tunca and Meriç River reached the highest level of flow and this area was always in the danger of flood.One of the most important previous floods in historical records happened in 1571. Edirne was damaged by floods and Edirne Palace and other important structures stayed under water.
By this flood which took place in II. Selim Period, Edirne Palace was flooded and its inside stayed under water. In this pre study conducted; it is seen that Edirne was damaged by floods and Edirne Palace and other important structures stayed underwater and the frequency of floods in the effect of disaster occurred in a few ten years or more.
TOKAT FLOOD, 12 June 1908
The
biggest flood disaster in our history was on 12 June 1908 in Tokat.In
1908,223 people died in the flood in tokat.459 buildings collapsed.
TURKISH REPUBLIC TIME
The most flood disasters in our country are in the Black Sea Region and in the ovals of the valleys of the big rivers.Flood disasters such as Artvin-Şavşat, Ordu-Perşembe, Bartın, Hatay-Yayladağı, Erzurum, Tekirdağ and Edirne have also been seen in our provinces in Eastern Anatolia and the Mediterranean region.These flood disasters caused serious loss of life and property. Houses and businesses are damaged. Agricultural land, drinking water and sewage systems, bridges and roads have suffered serious damages.

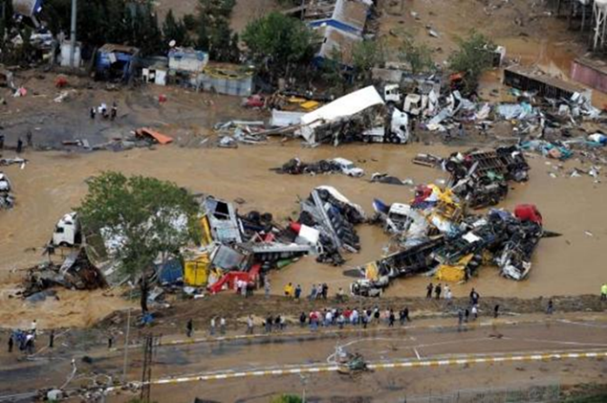
ANKARA FLOOD
It was the greatest disaster in history of TURKISH REPUBLIC.169 people died in this disaster.
2009 , Istanbul Flood

The 2009 Turkish flash floods were a series of flash floods that occurred on 9 September 2009 in and around Istanbul, Tekirdağ, and the rest of the Marmara Region of Turkey. The floods led to the death of at least 31 people and the cost of damage has been estimated as being in excess of $70 million. At least 31 people were killed across the region and dozens were stranded in cars or on rooftops and an unknown number remain missing. Three of the deaths occurred in western suburbs of Istanbul on 8 September, 21 people lost their lives in Istanbul on 9 September .
In some places the water reached a metre (3 ft) in height, cutting access to Istanbul's main airport and the highway running to Bulgaria and Greece. According to state-run news agency Anatolia News, one building collapsed, although there were no reported casualties. In north-west Turkey two bridges on the Bahçeköy–Saray highway were also destroyed by floods at the same time. More than 200 cars have been washed into the Marmara Sea and dozens of trucks damaged.
EDİRNE FLOOD , 2015
Heavy
rainfall hit Edirne, a northwestern province on the border with
Greece, causing the Tunca and Meriç riverbeds to overflow and
forcing hundreds of people to be evacuated from their villages to
safer zones on Sunday.
1,500 people had to evacuate in the
Karaağaç neighborhood and all residents living in Değirmen
Village. The evacuated residents were placed in a public gymnasium
hall, as experts expect the river discharge to rise to 2,500 cubic
meters per second.
The overflow of Tunca and Meriç
rivers as a result of heavy precipitation caused closures on the main
road in Karaağaç neighborhood, where 5000 people reside.
5. Landslides
Catastrophic landslides are widely distributed throughout Europe, with a great concentration in mountainous areas.
5.1. Italy
In Italy, slope failures occur every year, claiming lives, causing economic disruption, and producing different environmental problems. In Italy, intense or prolonged rainfall is the primary trigger of landslides, but also the hydrogeological instability due to human activities.
One of the major disaster was the Vajont dam, which happened on the evening on 9th October 1963.
It was caused by the fall of a 270 million m3 landslide from Mont Toc into the artificial lake, made by a 200m dyke.
This giant rock mass made the water into the bacin overflown.
After that the water caused the flood, the destruction of the city of the Venetian valley bottom, among which Longarone, and the death of almost 2000 people.
A lot of people also died in the district of Codissago and Castellavazzo.
Some aspects of human error that may have contributed to the landslide could have been due to the time in which this construction took place, as levels of technology were not well enough advanced to show accurate findings. When engineers knew that a tsunami could have been a possibility, they conducted a scale simulation to find out if the dam could hold back a tsunami wave if one did occur. They investigated this by changing the speeds at which a possible landslide could occur and observing whether the dam could hold back the height of the wave that these speeds could produce. However as this was not a computer simulation they could only estimate how long the landslide would take to fall. It is thought that if a computer simulation was possible at the time then a correct estimation of the size of the wave would have been produced, allowing the engineers to lower the reservoir levels accordingly. The Vajont dam disaster therefore was largely due to human errors, despite having an apparent natural cause, and if some of these errors could have been prevented, then although the landslide would have been likely to still occur, preventions could have been put in place such as evacuation, that would have saved the lives of those 2000 villagers below the dam. The volume of debris from the landslide was enough to destroy the reservoir, although ironically the dam itself still survives, with little damage.
5.2. Reunion
The mahavel landslide:
In 1965, 30 000 000 m3 of a part of the cliff of river channel of Mahavel, a district of Saint Pierre, fell.
The landslide didn’t cause victims but the noise was heard from Saint Joseph.
Waterfront Road landslide:
In 2006, in the waterfront road, 30000 m3 of rock fells on the road, there was 2 dead and 2 wounded. Since this big landslide, the government had put in place the building of the new waterfront road
The Salazie landslide:
The last year at Salazie, 10000 m3 rocks fell near to a river, the biggest rock weighed 2 t. There were no victims, but the road was stucked and it had scare people were living in the circus.

5.3. Romania
Landslides represent a common geomorphic hazard in Romania, threatening property and infrastructure mainly in the Carpathian Mountains and hilly regions, which account for more than 60% of the territory. In this regard Romania represents one of the countries most affected by landslides in Europe. Landslides are often associated with other major natural hazards, such as flood and earthquake. Although in Romania the number of human victims of this natural hazard is very low, landslide causes substantial damage to human property in affected regions. An increase in landslide frequency and magnitude has been observed in recent years, related to extreme rainfall resulting from climate change.
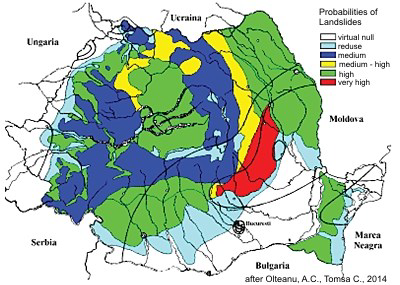
Unfavorable natural conditions such as: non-uniformity in the slope lithology, high slope gradients, and high rainfall rates combined with engineering works have accelerated local instability by increasing surface runoff and erosion. This has lowered the base level in the adjacent valleys/gullies by 1-2 meters, increasing the slide potential.
An example for the eastern part of Romania's Carpathian Mountains is the
Zemes landslide, which extends over 1.4 -1.8 kilometers in length, with a width of around 500 meters at the slope base and a total change in elevation of about 350 meters. This and similar slides cover 30-40 percent of the land on both sides of Tazlaul Sarat Valley. They have developed especially on soft or altered rocks. Unfortunately, these recurrent landslides produce an asymmetric shape to the valley, which increases the potential for landslide reactivation because of infiltration of water into the ground.
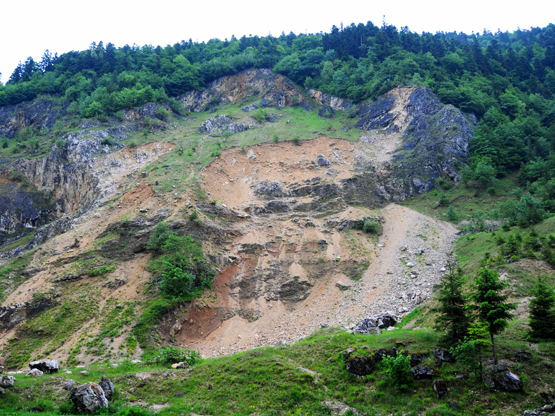

Most landslides in Romania occur as a result of a combination of:
1) poor forest management 2) intense rainfall.
5.4. Turkey
Earthquakes and landslides are the most serious geological hazards in Turkey because of the unprecedented losses that result from these hazards. Frequent landslides in this country often cause significant harm to people and property. landslides occur frequently due to climatologic geomorphologic, and geologic conditions. The landslide phenomenon in Turkey is mostly observed in the Eastern Black Sea Region in the Black Sea Region, mostly in the Central and Eastern Anatolia RegionsThe losses caused by landslides in Turkey are extremely important. Landslides seen in many places of the country almost every year lead to many loss of life and property
At the beginning of these losses are human losses. Between 1970 and 1995, 236 of our citizens lost their lives as a result of these movements, including mudflows.As a result of the landslides, the amount of animals consumed and the number of homes that come into the house are very high. Between 1971-1989, the 1960 building was partially damaged or completely destroyed. Turkey is located in a region with the highest rainfall where the landslides mostly occur. Only in the last 30 years, more than 2000 landslides occurred in the region.
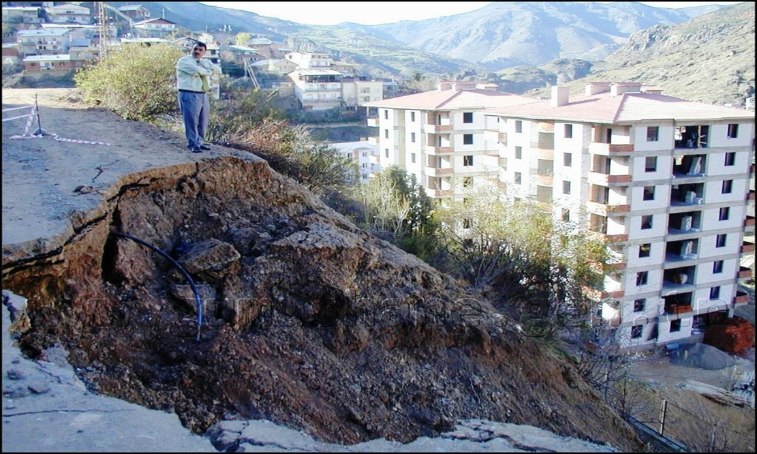
1985 WEST CARIBBEAN MARITIME DISTRICTS: Following the extreme snowy winter season, 1684 houses in Zonguldak, Kastamonu and Sinop province suffered landslide damage, which suddenly appeared in the beginning of spring as snow.

23.06.1988 ÇATAK TEXTURE: Catak village in Trabzon Province, Turkey, is a scattered collection of houses on the main Trabzon-Erzurum road, 30 km inland from the Black Sea coast. The village is sited on the valley floor of the Degirmen River, which has incised deeply through an alternating sequence of Upper Cretaceous flysch deposits and volcanic lavas to yield steep terrain with a relative relief of about 1000 m. The confined nature of the valley floor at Catak, together with the additional constraints imposed by a river confluence and a cemetary, necessitated that improvement of the road in 1984 involved an alignment on the eastern margin of the valley. This cut into the base of a slope 225 m high, standing at an overall angle of 40°. On 22 June 1988 the colluvial materials mantling the lower part of this slope failed and blocked the road. A grader was despatched to the scene, but clearing operations were postponed until the morning because of fears that continuing heavy rainfall might cause further failures.
The Catak landslide received widespread media coverage as the death toll was initially estimated as being up to 300 people.
19 / 20.06.1990 TRABZON-GİRESUN-GÜMÜŞHANE TERMS:
The events of landslides and floods, which caused the death of 65 people on each of the three villages and caused massive loss of money, came to fruition.
07 / 08.08.1998 TRABZON-BEŞKÖY LAYER: 50 people lost their lives and 101 houses were destroyed. Trabzon, which is located in the northeast region near the Black Sea, is one of the areas where landslides most commonly occur. Between 1950 and the present, there have been more than 270 landslides in Trabzon. The factors affecting the occurrence of landslides are the morphology of the region, geological structure, weathering of rocks, meteorological characteristics, settlement types, and various types of excavation work. Heavy precipitation, sloping topography, and the removal of forests for agricultural purposes increase the landslide risk.
AYVACIK LANDSLIDE 12 / 02/2017
Following the recent earthquake of 5.3, a mountain slip on the mountain near the Babakale Harbor in the Ayvacik district came to the scene. There was a landslide during an earthquake on a steep slope at Babakale Harbor, which is very close to the earthquake zone.
6. Storms
Storm activity tends to be severely underestimated, but there are severe risk for storma and cyclones in Europe
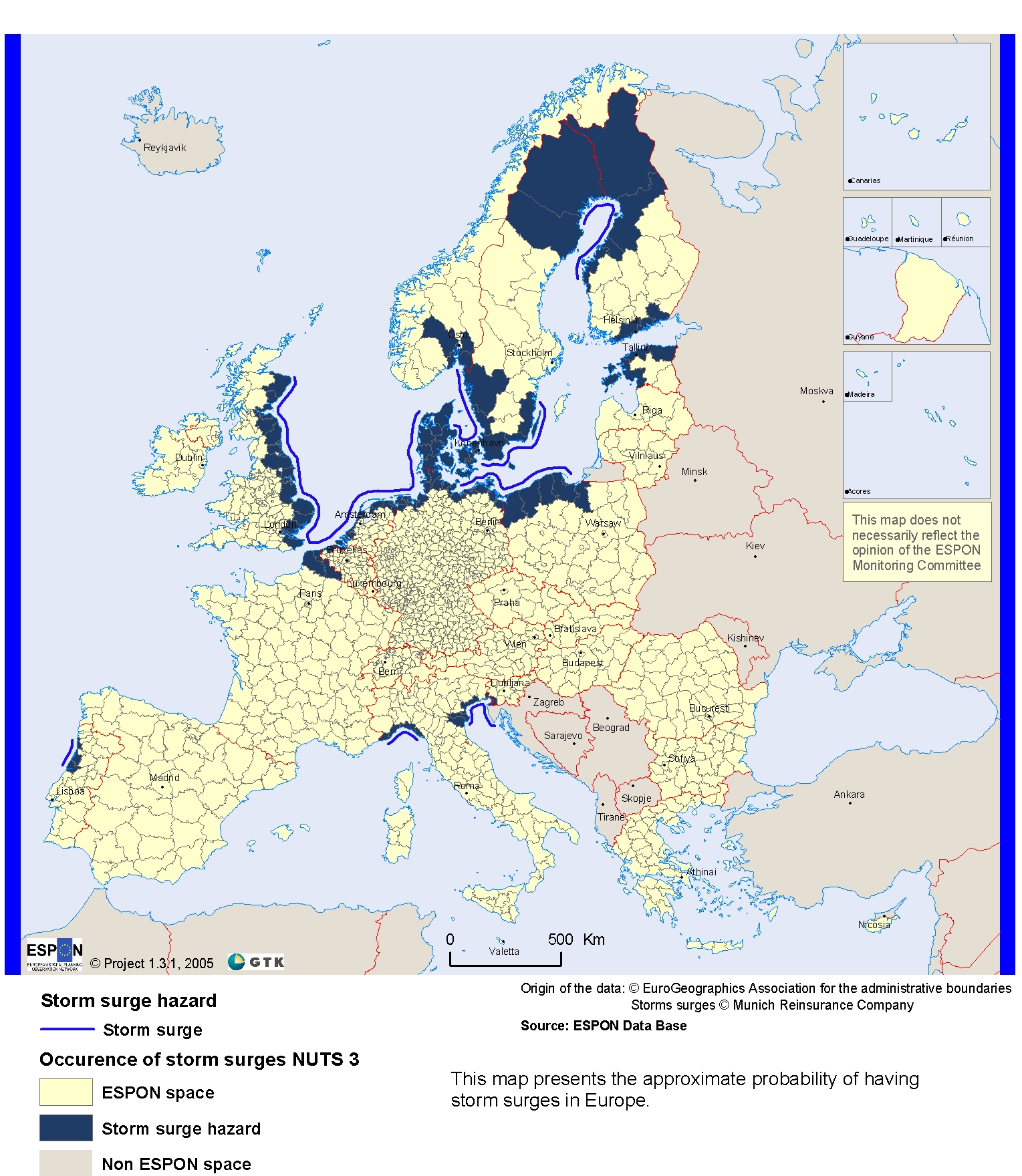
6.1. Reunion
We
will talk about 3 historicals cyclones of our country and about the
last cyclone:
Hyacinthe(1980)
Firinga(1989)
Gamède
(2006)
Carlos(2017)
- Hyacinthe in 1980 :
In 1980, Hyacinthe marks reposts by his chaotic trajectory during 2 weeks.The depression passes several times stagnates on the same time. The cyclone went through three time very close to the Island . it is still low intensity during its first passage the 18th january. It is then only a tropical disturbance.Hyacinthe then evolves into tropical cyclone . He made a loop and returned in the direction of the island.And passes in the south west of « La pointe des galets » before it go away by the East. Then the third passage took place after a new loop, Hyacinthe passes too near of the reunion Island..Hyacinthe has plunged Réunion Island under waters during these 2 weeks and killed 25 people. For twelve days, the circulation of the storm produced cloudiness and thunderstorms over Réunion. The cyclone even beat several international records of precipitation, since the island remained 12 consecutive days in the rain generating up to 5181mm of precipitation.
-Firinga in January 1989
Firinga was on the Island in the night of the 29th to the 30th January 1982 . The suth of the island was more touched (affecting) with winds reaching ; 216km /h in Sait-Pierre . The overfloxing of rivers inflated by rains extracted and destructed a lot of houses , roads and trees .
The balance sheet was tree missing people , 52 wounded , and thwo deaths.The cyclone Firinga at night from Sunday, 29 till Monday, January 30th, 1989 transformed the South of the island into a vast torrent of mud. In the Plaine des Cafres he(it) fell 700 mm of water within 24 hours

-Gamède in February 2006
The tropical cyclone GAMEDE will stay in annals by its extremely size and its trajetory which made him approach itself twice coast from us . So Reunion island beat , 27 years after HYACINTH , its own worl records of precipitation during 3 at 9 days .
GAMEDE, classified intense tropical cyclone during its maximal phase, stayed at 400 km of Reunion during almost 4 days, with an extremely vast sphere of influence in term of winds and precipitation. Winds were certainly strong on a long , but did not have of very exceptional nature (167 kph in Bellecombe , 163 kph in la Plaine-des-Cafres, 140 kph to Gillot). On the other hand, rains, although not having known extreme peaks of intensity, were very regular and very plentiful in all the tops of the island, producing by accumulation of the even exceptional remarkable blades of water on durations of one in several days .
After the first passage of GAMEDE , we could already make a first balance assessment : - A badly wounded person. - The destruction of the bridge(deck) of the river Saint-Etienne which connects(binds) Saint-Louis and Saint-Pierre , following the break of a natural roadblock . The southeast cut in two. It is the strong image which will stay of this cyclone. - 100 000 homes without electricity, and so deprived of water - 40 000 subscribers deprived of landline telephone - Around thirty submerged radiers - Several landslides - Approximately 250 people accommodated in the municipal centers - A zone flooded to saint-Suzanne
At night of 26 in 27, the meteor decides finally and comes down southward . It makes then a second passage as closely as possible to Reunion at 250 km on the West in the evening of 27. The West of the department is so touched . Except the cyclonic swell, which is then at his/her/its maximum with a 11,7 meter height measured in the Port(Bearing), this second passage generates a little less strong rains . The balance sheet grows heavy: - we regret 2 victims, among whom the one is taken by streams while she tried to cross one radiate by car - the roads of Salazie and Cilaos are cut - several families are evacuated in Mare à Poule d’eau, Ilet Quinquina and la Colline.
Globally, on all the tops of the island, and if we refer to the accumulations on 4 days, the values of the episode GAMEDE are close or superior to the fact than we were able to observe on the occasion of the cyclone HYACINTH . For exemple , in 24 hours : 1628 mm in the Crater Commerson, so approaching the official world record of 1825 mm measured in Foc-Foc with DENISE's passage in 1966. We also raise1489 mm to Hell-Bourg
-The storm ‘’Carlos’’passed as close to Réunion Island in Tuesday 7th February with gusts of winds enter 100 and 130 kph. It touched principally the North and the East of our country Tuesday and the West ans the Southwest in Wednesday. In Tuesday ,the prefect announced the closure of all schools in the Island as a precaution.
So , it rained a lot in somes cities and we had a ‘’Raw vigilances alert’’ because somes rivers like revers Marsoins or Langevin were flooded.
Also , Carlos caused a lot of incidents :
- Trees fell down because of gusts of wind , it provocated some accidents and some
roades were blocked.
- We had some screes who blocked roades too.
-Somes peoples didn’t have electricity because electrics cables were broken .(4000 houses)
- Somes peoples didn’t have water for a moment also , like in La Plaine des Cafres for Example.
Also, the ports were closed because of the swell.
And this cyclone caused some injured peoples by accidents.
7. Fires
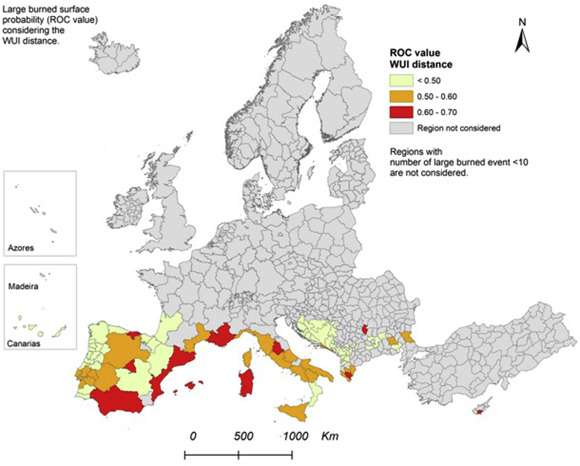
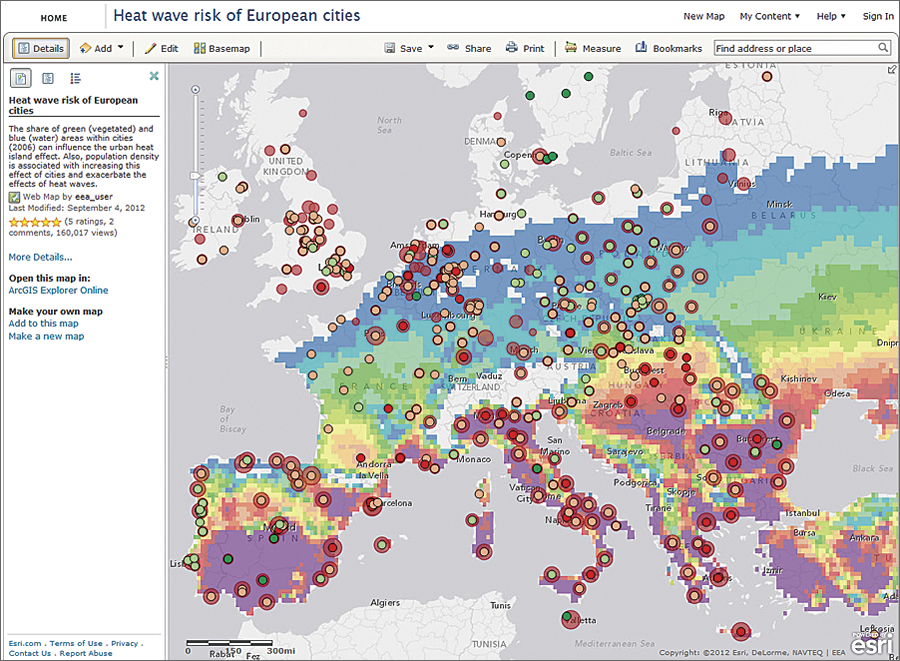
7.1. Greece
So let’s start by saying how a fire starts: campfires, smoking, lightning, debris burning, fireworks and arson are the most common causes. There are also a couple of factors that can make a wildfire bigger, like wind, slope, temperature and humidity. In case a fire happens stay calm. Immediately call the Fire Brigade (calling number in Greece: 199) and give a detailed account of your position and the wildfire's position, describe the attributes of vegetation that is burning, determine the wildfire's direction of spreading, do not hang up before giving all the necessary information to the fire service.
The
Hellenic Fire Service (Pyrosvestiko Soma) is the national agency of
Greece for fire and rescue service. It is part of the Ministry for
Citizens’ Protection. It is responsible for putting out the fires
that occur in Greece. But if someone doesn’t take care during a
fire, it is really easy for them to lose their life, the most serious
consequence of fire, which is neither valued nor restored. In cases
of fire, in which human lives are in danger, the aim of the
firefighters is primarily to protect and rescue people, and then to
protect forests, houses, social structures etc. However, the greatest
danger from a fire focuses on human health and specifically on
vulnerable groups such as children, elderly, and people who suffer
from chronic respiratory problems.
One
of the greatest fires that ever happened in our country is the Great
Fire in Thessaloniki. The greatest fire that occurred in Thessaloniki
happened in 1917, almost a century ago, and was not extinguished for
13 days (5 of August – 18 of August).
Other
great fires are the 2007 Forest Fires. The 2007 Greek forest fires
were a series of massive forest fires that broke out in several areas
across Greece throughout the summer of 2007. The most destructive and
lethal infernos broke out on 23 August, expanded rapidly and raged
out of control until 27 August, until they were put out in early
September. The fires mainly affected western and southern
Peloponnese, as well as southern Euboea. The death toll in August
alone stood at 67 people. In total 84 people lost their lives because
of the fires, including several fire fighters
The Big Fire of Thessaloniki ,in 1917
7.2. Italy
During the summer of 2003 there was an increase of temperatures that affected all Western Europe. In fact, a lot of temperature records were broken. For example, in Amareleja (Portugal) it reached 48°C.
The main cause was the low pressure area around the middle latitudes of the Atlantic Ocean. In particular, the heat was a result of the western European seasonal lag from the maritime influence of the Atlantic warm waters with hot continental air and strong winds from the South.
There were lots of effects on agriculture, mainly in Southern and Western European countries. The production of both wheat and grapes was subjected to a massive reduction. Moreover, the Mediterranean Sea was affected by a big impact on its ecosystem. This caused anomalies on sea surface stratification in the Mediterranean Sea and on the surface currents. The Atlantic Ionian Stream, a seasonal current of the central Mediterranean Sea, was changed in its path and intensity due to the warmer temperatures. The heatwave has also influenced indirectly the reproduction of some fish species living in Mediterranean Sea.
In Italy that summer was among the warmest in the last three centuries and the maximum temperatures of July and August remained above 30 °C. Moreover, the high humidity intensified the perception of heat and population suffering. Here there were over 4000 deaths related to the heat wave and 18000 more than the previous year.
In particular, these are the highest temperatures reached in Italy in 2003
7.3. Reunion
In island of Reunion, forest fires are very common.The wind and drought of recent years favors their extension and the excavated areas where it is located are often inaccessible. Here is the record of the damage of the last years:
- 2010 : about 951 ha burned
- 2011 : about 3000 ha in the biggest forest fire of the the story of Reunion Island.
- 2012 : 266 ha for 326 Fire start
- 2013 : 324 ha for 496 Fire start
- 2014 : 245 ha for 447 Fire start
- 2015 : 198 ha for 262 Fire start
- 2016 : Since September 15 , 164 ha for 87 interventions.
- By the wind who stir the fire. The wind pushes the fire and helps him to spread
- By the basement. The heat passes under the ground to touch other trees.
To counter this disaster, there are several techniques used. There are firefighters who water the fire, there are fire cuts, they are bands of land where there are no vegetation And there's the Dash 8, it's an airplane that drops water on the fire.
7.4. Turkey
From past to now there were many fires which affected us.. We can list the fires that have caused huge losses until today.
The fires of Istanbul
The fires of Istanbul, reaching back 300 thousand years ago, were unlike tragedies in the world.History gave the fires of Istanbul the name of dragon which surrounded the city. At some times this dragon destroyed the half of Istanbul city and left thousands of people in wreckage. Fire was a disaster for Istanbul. This disaster did not only harm the welfare and wealth of the citizens but at the same time damaged their ease and happiness.
Istanbul, in which great historical fires took place, consisted of all wooden buildings since the Byzantine period. Many fires broke up in Istanbul, like those in the other cities of First and Medieval Ages. The city became more and more important after the Ottoman Conquest. The population of Istanbul increased day by day. The city gradually developed, and streets and squares became smaller due to the new constructions.Therefore fire hazard grew more in the city.
25 August 1515 Great Fire of Istanbul: This fire was extinguished when it stood against Gedikpaşa hamam in the afternoon after the Ashes of Bethesda and the ashes of many shops. It is reported that this fire came from Yavuz Sultan Selim. After this date, the great fires of Istanbul have been repeated in the form of a cataclysmic sequence which is now frequently found in the Ottoman city. These fires have led to the change of the city of Istanbul very often in terms of urbanism and the disappearance of the books with many books which will explain our history.
September 19, 1569 Great Fire of Istanbul: This time the great fire of the Second Selim Devra came out of the Jewish quarter and could only be exploited on 26 September after seven days and seven nights. According to some foreign vesikalara this terrific fire burned 360000 houses
Alleged. This fire was not able to come because the janissary network of Sokullu, Cafer Aga, was ill, so that the new janissaries who had not been able to get started had spread fire on the beginning of the plunder and therefore Cafer Aga was dismissed and Emir Ahhur Siyavuş Ağa was appointed instead.
September 2, 1633 Great Fire in the City Burning a Bastard One Great fire in a ship in Cibali has been separated from Cibali to Ayzkapısı and three branches after Mustafa Pasha Bazaar. A branch of Kadi Fountain burned down the district of Sultan Selim, the second branch along the coast to Unkapam and Zeyrek Yokusu from there, and the third branch to Sarıgüzel after the burning of Saraçhane. The sultan of the period put forward the "Tobacco Legion" and claimed that all the horses were closed.
THE REASONS OF FIRE
The houses’ being made of wood and their lining so closely to each other on streets, the narrowness of the streets, and the lack of water and extinguishing agents resulted in the houses’ burning to the ground almost across the city.
FIRE TOWERS
Fires were announced by means of flags in Bayezid and Galata Fire Towers. The fires belonging
Janissary water pumpers (Yeniçeri tulumbacıları) period 1714– 1826
This
second period went on till the abolishment of the guild of
janissaries in 1826. The historians recorded that 44 great fires had
happened and in these fires 7000 buildings, inns, Turkish baths and
madrasas had burned. In this period, firefighting was initiated.
These fires were extinguished immediately by
tulumbacılar(firefighter)
Third period; Fires belonging to the period of district water-pumping and city halls (1826-1874) When the guild of janissaries was abolished in 1826, the guild of Ottoman water-pumpers would have been abolished, too. The important fires of this period. Fires that left traces before republican history: In 1874 Samatya fire burned 687 buildings.In 1874 Üsküdar fire, 365 buildings burned.1877 fire came out of court, 121 buildings burned.1200 buildings burned in the 1890 Pendik Fire.1890 The fire came out of the rampart, 1 mosque, 35 shops and 70 houses were completely ash.1892 Fire came out in Karabas neighborhood, 25 houses became ashes.In 1896 the fire came out around Dibek in Karabas District, 45 buildings were ashes.In the 1903 Eagle fire 1121 buildings burned.1908 1500 buildings burned in the fire of the gin.5500 buildings burned in 1911 Aksaray fire.In the fire of 1918 Fatih Cibali 7500 buildings were burnt.
(Turkish for fried eggplant) is an eggplant dish from the Turkish cuisine. It is such a common dish during summer months that this season used to be called "patlıcan kızartma ayları" (fried eggplant months) in Ottoman Istanbul where this generalized frying caused huge fires and destroyed the street due to the abundance of old wooden houses.: When the eggplant was frying, a fire broke out.In this fire 110 buildings were burnt.
August 23, 1927 Üsküdar Valide'i Waste Fire: Fire again in a wooden house has caused the burning of ashes in 201 houses.
January 22, 1929 Fire of Tatavla (Present Liberation): In this fire where the firefighters came in the winter and the firemen had difficulty in getting water, 207 buildings were burnt.
20 June 1937 Beşiktaş Uzuncaova Fire: 31 houses were completely burned in the fire in the neighborhood consisting of two storey wooden houses.
1952 Adana Çukobirlik Cotton Factory Fire: A $ 2,500,000- loss was incurred in this fire and was fully compensated by the insurance company.
1954 Fire of the Kapalıçarşı: In the bazaar, 744 shops were totally burnt, 2034 partly in the 1290 shops and 30 shops outside the bazaar were completely burnt. The fire grew out of control because of the fireman opening both doors of the Grand Bazaar. Insurance companies pay $ 2.650.000- $ compensation. This fire insurance industry, which accounts for 30% of Turkey's insurance portfolio, has been an important test
A large number of fire examples can be shown from 1941 to the present day. Especially the increase in activities and numbers of big businesses in social life has caused the increase of fire damagefrequency and severity.For example :
ANTALYA FIRE 2 August 2006
The fire, which broke out Friday and was fanned by strong winds, destroyed part of the village The blaze, which destroyed about 4,000 hectares (10,000 acres) of woodlands, broke out most probably after winds reaching up to 70 kilometers per hour (43.5 miles per hour) tore down power lines.
About 1,300 people, helped by fire-fighting helicopters and airplanes, were battling the blaze that raged between Serik district and the coastal town of Manavgat, where several large holiday villages are located.Aircrafts dropped loads of water to douse the flames amid a thick pall of smoke hanging over the Mediterranean hillsides in what one official described as the worst fire Antalya province had ever faced.
Fire in Haydarpaşa Station 28.11.2010 :
The historic roof is completely burned The fire at Haydarpaşa Train Station was taken under control after about an hour of work. The fire broke out at 15:30 and the fourth floor suffered extensive damage. A fire extinguishing vessel connected to the coast guard also supported the fire extinguishing activities attended by all the fire brigade teams on the Anatolian side. It is known that insulation works on the roof cause fire.
SOMA MINE FIRE, May 17, 2014
In total, 301 people were killed in what was the worst mine disaster in Turkey's history. The fire occurred at the mine's shift change, 787 workers were underground at the time of the explosion. After the final bodies were pulled from the mine on May 17, 2014, four days after the fire.
Trabzon-Sürmene Fire 08.01.2017
An
area of 15-20 hectares is affected. Fire caused by a picnic.
50 firefighters intervened.
8. Invasive species
The cumulative number of alien species introduced has been constantly increasing since the 1900s While the increase may be slowing down or levelling off for terrestrial and freshwater species, this is certainly not the case for marine and estuarine species. A relatively constant proportion of the alien species established cause significant damage to native biodiversity.
While
the majority of the approximately 10 000 alien species recorded in
Europe (DAISIE project) have not (yet) been found to have major impacts,
some are highly invasive.
While
invasive alien species are recognised as a major driver of biodiversity
loss, the issue of 'alien species' may in the future need to be
considered in the context of climate change and particularly adaptation.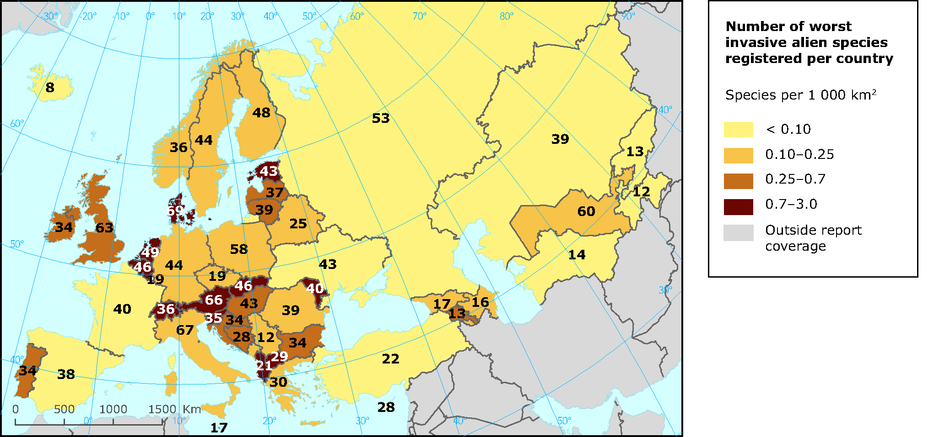
8.1. Portugal
In this work we will talk about three different types of plants and one animal in Portugal.
Our goal is to give you some information about their characteristics and important facts .
I
hope you like it !
Mimosas
Evergreen tree, with grey-green bipinnate leaves and bright yellow spherical flower heads.
Characteristics that aid invasion:
It propagates vegetatively, forming vigorous sprouts from the stump or roots after being felled.It also reproduces by seed, producing many seeds that accumulate in numerous seed banks and remain viable in the ground for many years. The seeds are dispersed by animals, mainly birds and ants, and sometimes by strong winds which lead to the formation of dispersed and/or far away invasion foci from the invaded areas. Most propagules, however, accumulate underneath the tree, forming a numerous seed bank. It germinates aggressively after fires.
Native
distribution area:
Southeast Australian states of New South Wales, Victoria and
Tasmania. Distribution in Portugal: Mainland Portugal (all
provinces), Madeira archipelago (island of Madeira).
Jacintos
de água
Aquática herb, floating, with swollen leaves and very flashy blue/violet flowers.
Characteristics that aid invasion:
Eichhornia crassipes has an extremely rapid growth: in adequate conditions, the species may double its population in 5 days. The growth rate is higher in springtime, reducing in autumn due the decrease in temperature and formation of frost. It may survive on land if there is a large amount of water available.
It may easily propagate vegetatively, through rhizomes or small fragments from which a new plant may generate. Each fragment may be dragged by the water flow and originate new invasion foci far from the original population.It also propagates by seed. The seeds can be viable for a long time (up to 20 years) and due to their small size, they are easily swept up by the current. The seeds are also dispersed by aquatic birds.
Native distribution area:South America, in the Amazon Basin.
Distribution
in Portugal:Mainland
Portugal (Douro Litoral, Beira Litoral, Estremadura, Ribatejo, Alto
Alentejo), Azores archipelago (islands of Flores, Faial, Graciosa,
Terceira and São Miguel).
Eucalipto
Evergreen tree, aromatic, with young bluish-green leav
In Portugal, the most area occupied by this species corresponds to plantations by Man and not natural dispersal/invasion. The species is included as invasive because, on one hand, it has seen its invasive behaviour in many situations in the country and, on the other hand, its wide distribution creates a high propagule pressure which constitutes an increased risk. Additionally, this species is considered invasive in many regions with Mediterranean type-climate.
Characteristics that aid invasion
Species of very fast growth. It propagates vegetatively, sprouting vigorously from stumps (used in the pulp industry). In Portugal, for a few years now, seed germination has started to be observed, including outside the stands, mainly after the plantation abandonment and wildfire occurrence, which create empty niches.
Native distribution area
Southeast Australia and Tasmania.
Distribution in Portugal
Mainland
Portugal (all provinces), Azores archipelago (islands of São Miguel,
Santa Maria, Terceira, Graciosa, Pico, Faial and Flores), Madeira
archipelago (Madeira and Porto Santo islands).
Háquea-picante
Evergreen shrub or small tree, with robust and very sharpneedle-like leaves.
Characteristics that aid invasion:
It reproduces by seed. Frequently, the seeds remains enclosed within the fruits, which in their turn remain grasped to the tree, throughout the plants’ lifetime. They are released when the tree is burned or dies. The seeds are then projected to great distances, creating new invasion foci that frequently occupy very extensive areas.
Native distribution area:
Southern Australia.
Distribution in Portugal:
Mainland
Portugal (Trás-os-Montes, Minho, Douro Litoral, Beira Baixa, Beira
Litoral, Estremadura, Ribatejo, Baixo Alentejo, Algarve.
Lagostim vermelho
It is a freshwater crustacean that has a reddish or brownish color. It has five legs, breathes through gills and can remain some time out of water.
Characteristics that aid invasion:
Louisiana red snapper causes serious negative impacts on animal and plant life in the habitats it invades and quickly becomes the main species. It fiercely competes with habitat, food and predation with native species of crayfish (in Portugal with Austropotamobius pallipes or white-footed crayfish), contributes to the reduction of macrophytes, invertebrates, amphibians and fish and causes changes in the food chain of habitats Aquatic In short, it reduces habitat biodiversity. Due to excavation, it causes changes in hydrology and soils, including loss of water in rice paddies, reservoirs, etc., with negative implications for the crops produced.
DISTRIBUTION :This exotic and invasive species is native to North America. It is present in several European countries, including Portugal, but also in Africa, Asia and South America.In Portugal it is found in all hydrographic basins
Conclusion: In mainland Portugal, over the last two centuries, and especially in more recent decades, the number of exotic species (including causal, naturalized and invasive) has increased significantly, currently amounting to about 670 species*, which corresponds to approximately 18% of the total native flora (Almeida and Freitas 2012). In the archipelagos of Madeira and the Azores the number of exotic species is also very high. For the Madeira and Savage Island archipelagos 430 exotic species have been recorded, equivalent to approximately 43% of all the vascular plants in these archipeligos (Jardim and Sequeira 2008). In the Azores, of the approximately 1000 species of vascular plants, around 60% are exotic (Scott and Smith 2006). We were able to understand and learn some facts about some species , including their origin and present location in the national territory